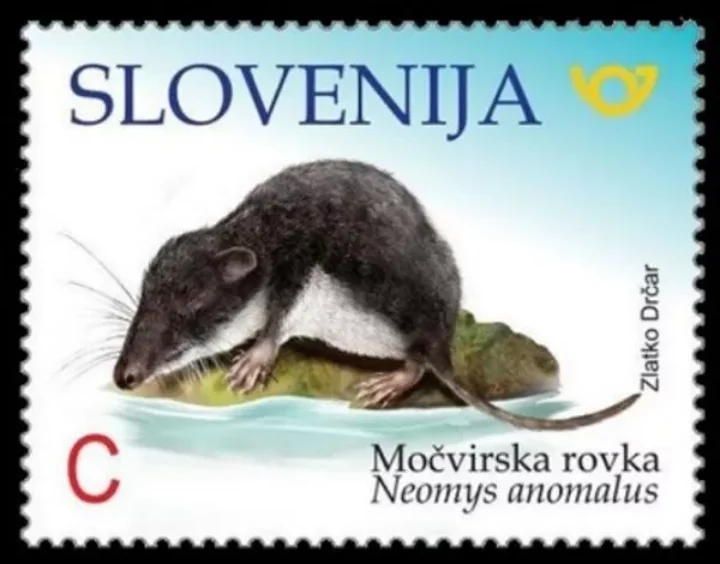
Slovenia stamp year 2018 Fauna Mediterranean water shrew Neomys anomalus ☀ MNH**
Here are the key details about the Slovenia 2018 postage stamp featuring the Mediterranean water shrew (Neomys anomalus):
🦦 Slovenia 2018 Fauna Stamp — Mediterranean Water Shrew
- Country: Slovenia (Pošta Slovenije)
- Issue Date: 28 September 2018
- Theme / Series: Fauna of Slovenia — part of a set of stamps depicting endangered or notable mammals (including lynx, mountain hare, otter, least weasel, and the Mediterranean water shrew)
- Species Depicted: Mediterranean water shrew (Neomys anomalus) — a semi-aquatic small mammal found in wetland and riparian habitats
📮 Stamp Specifications
- Designer / Illustrator: Zlatko Drčar
- Printing: 4-colour offset in self-adhesive sheets of 50 stamps
- Format / Size: Approximately 30.80 × 23.76 mm
- Perforation: Serpentine die-cut (self-adhesive)
💶 Face Value
- This stamp is part of the definitive (regular postal) issues from 2018 with denomination C (used for specific postal rate) rather than a fixed euro amount printed; these letter-rate stamps correspond to current postal fees at time of issue. In many collector listings it appears with catalog numbers around Michel 1287–1289 for this and related values in the set. In modern Slovenian stamps, face value “C” typically means it pays a standard domestic or international rate under letter classes (for example, domestic letter up to a certain weight).
• In some dealer listings it’s shown alongside a numeric value like ≈ €1.79 (reflecting the typical selling price for a mint, never-hinged stamp) but that is not the postal face value printed on the stamp itself.
📌 Collecting & Catalog Info
- The Mediterranean water shrew design is usually listed as one of the definitive wild animal (fauna) stamps issued in 2018.
- Stamp catalogs such as Michel or Scott assign specific catalogue numbers to each value (e.g., around #1288 for this motif).
- Collector value for a mint, never-hinged (MNH) stamp today is typically modest (close to face value plus a small premium), as it’s a fairly modern, common issue.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.