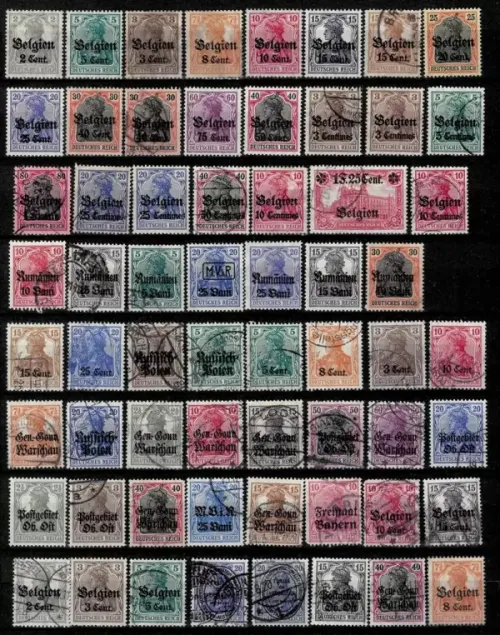
WWI German Occupations and levant year 1900/1920 stamps
During World War I, the German Empire occupied various territories and regions for strategic, political, and economic reasons. Some of the notable German occupations during WWI include:
- Belgium: German forces invaded Belgium in August 1914 as part of the Schlieffen Plan, aiming to swiftly defeat France. The occupation of Belgium led to widespread destruction and atrocities, including the burning of towns and villages.
- Northern France: Large parts of northern France, including regions like Alsace-Lorraine, were occupied by German forces during WWI. The occupation led to significant hardships for the local population and was marked by trench warfare and battles such as the Battle of Verdun and the Battle of the Somme.
- Eastern Europe: Germany occupied several territories in Eastern Europe during WWI, including parts of Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. These occupations were part of the Eastern Front of the war and aimed at expanding German influence in the region.
- Occupied Serbia: Following the Serbian defeat by the Central Powers, including Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Bulgaria, Serbia was occupied by German and Austro-Hungarian forces during WWI.
- Occupied Romania: After Romania entered WWI on the side of the Allies but suffered defeats, parts of the country were occupied by German and Austro-Hungarian forces.
- Occupied Russian Territories: During the chaos of the Russian Revolution and subsequent civil war, German forces occupied various territories in Russia, including parts of Ukraine, Belarus, and the Baltic states.
- Occupied Ottoman Territories: German forces also supported the Ottoman Empire in its campaigns in the Middle East during WWI, leading to the occupation of territories such as parts of modern-day Iraq and Syria.
These occupations had significant consequences for the occupied territories, including economic exploitation, population displacement, and social upheaval. The end of WWI and the subsequent Treaty of Versailles led to the withdrawal of German forces from most occupied territories and the redrawing of borders in Europe.